Safety, Health and Environment
Free
- Business, Operations, Safety, TPM
- 159 (Registered)
-
(1 Review)
02
Apr
Chapter 11 of TPM Instructor Course.
The basic approach to safety, health, and environmental management in TPM is multi-pronged. A zero-accident scenario must be achieved by eliminating every conceivable hazard or concern that might give rise to a safety incident.
SHE activities described in this chapter and elsewhere in this manual are only examples, and the decision as to whether or not to adopt a particular activity is left entirely up to the facility or company where the activity is to be performed.
Next Chapter – TPM Instructor Course
Curriculum
- 5 Sections
- 25 Lessons
- 10 Weeks
Expand all sectionsCollapse all sections
- The Importance of Safety, Health and the Environment2
- Safety Programs9
- 3.1Health and Safety and their Relationship with Productivity and Economy
- 3.2Workplace Incidents and Problems to Be Solved in Creating a Safe Workplace
- 3.3Why do People Fail to Observe Rules Properly?
- 3.4The Basic Approaches to Safety
- 3.5The Need for Full Involvement of All Employees
- 3.6Building a Companywide Safety Management Structure
- 3.7Safety Activities Combining Management and ahe Shop Floor
- 3.8Using Safety Tags and Maps
- 3.9Examining Past Accidents and Analysing Data
- Creating Worker-Friendly Workplaces3
- Towards a Recycling-Oriented Society5
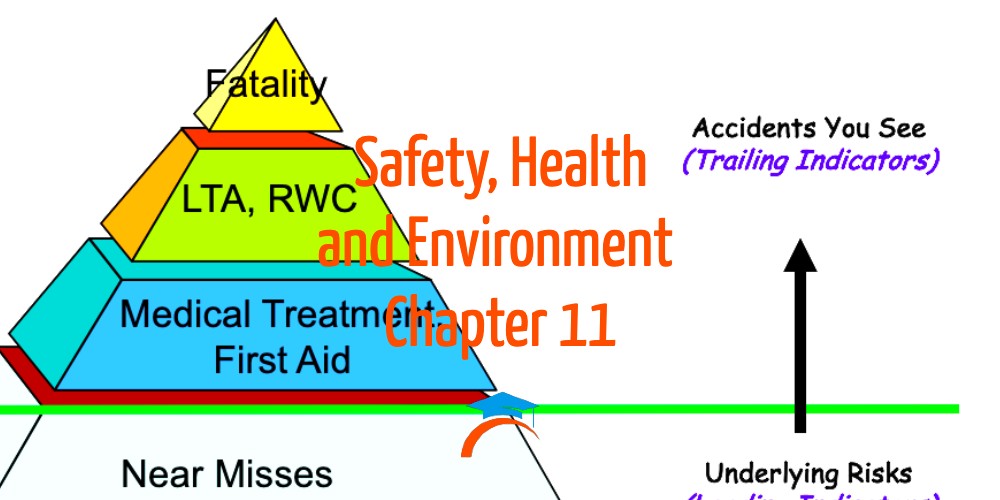
- Management Indicators6
- 6.1Result Based SHE indicators
- 6.2Establishing a Safety Management Organization and Safety Committees
- 6.3Items to Be Checked at the Preparation Stage
- 6.4Investigating and analyzing, reviewing hazards, and making improvements
- 6.5Strategies for dealing with points that are difficult to resolve
- 6.6Reducing fatigue








